Table of Contents
- Introduction;
- What is Edge Computing?
- Unlike conventional cloud computing that relies on distant data centers, Edge Computing brings computational capabilities closer to where data is generated. This enables faster decision making and improved performance.
- In this exploration of Edge Computing, we will delve into the core principles that drive this shift in paradigm. We will discuss the decentralized distribution of computing resources and the integration of edge devices with the Internet of Things (IoT).
- 1. Overview;
- 2.Key Components;
- Edge Devices; These are physical devices situated near the data source, such as sensors, IoT devices and smartphones. They possess computational power to process data locally.
- Edge Servers/Gateway Devices; Positioned at the network’s periphery, these devices collect and preprocess data before transmitting it to the central data center or cloud. They act as intermediaries between edge devices and the cloud.
- Cloud; While Edge Computing emphasizes local processing, it often collaborates with the cloud for tasks that benefit from centralized computing power, storage capacity or long term analytics.
- 3.Advantages of Edge Computing;
- Reduced Latency; By processing data in proximity to its source, Edge Computing significantly minimizes latency. This enables real time or near real time responses crucial for applications like IoT, autonomous vehicles and augmented reality.
- Bandwidth Optimization;
- Edge Computing helps minimize the need to transfer large amounts of raw data to central servers, which in turn optimizes network bandwidth and reduces congestion.
- Improved Security and Privacy; By processing data locally, Edge Computing enhances security by minimizing the exposure of sensitive information during transmission. It also provides better control over data privacy compliance.
- Scalability; With Edge Computing, distributed scaling becomes possible. This means that computational resources can be added locally as required, resulting in a more flexible and scalable infrastructure.
- Enhanced Reliability; Local processing enhances system reliability by reducing dependence on a centralized infrastructure.
- Working of Edge Computing
- 1.Data Generation at the Edge;
- Local Data Processing;
- Instead of sending all the data to a central cloud server for processing, edge devices perform initial data processing locally. This involves tasks such as filtering, aggregation and basic analysis.Reduced Latency;
- One of the main advantages of edge computing is that it reduces latency. Since data is processed closer to its source, there is less delay in receiving insights or taking actions based on the processed data.
- Edge Nodes or Gateways;
- Transmission of Data to Centralized Cloud (Optional);
- Real Time Decision Making;
- Use Cases;
- Internet of Things (IoT); Edge computing plays a crucial role in IoT applications, where devices generate massive amounts of data that need to be processed quickly. This is especially important in scenarios like smart homes, industrial IoT and healthcare.
- Autonomous Vehicles; Edge computing empowers on board processing for real time decision making in autonomous vehicles, enhancing safety and responsiveness.
- Healthcare; In the healthcare sector, Edge computing enables rapid analysis of patient data from medical devices, ensuring timely responses and reducing the burden on central servers.
- Smart Cities; Edge computing is an essential component of smart city initiatives as it enables local processing of data from diverse sensors and devices. This contributes to efficient city management.
- Challenges;
- Standardization; The landscape of Edge computing lacks standardized protocols, making interoperability between different edge devices and systems a challenge.
- Security Concerns; Extending computing power to the edge introduces new security vulnerabilities that necessitate robust measures to protect local devices and data.
- Management Complexity; Managing a distributed network of edge devices while ensuring synchronization poses logistical challenges.
- Future Outlook;
- Edge Computing is poised for widespread adoption as technology progresses.
- The expansion of 5G networks, the widespread use of IoT devices and the growing need for instant data processing all play a role in driving the ongoing advancement and integration of Edge Computing across different sectors. Essentially, Edge Computing signifies a move away from a centralized computing framework towards a more dispersed and decentralized approach. It provides an effective solution to meet the requirements of our progressively interconnected and data oriented society.
- Conclusion;
- To sum up, Edge Computing is at the forefront of innovation and offers a transformative approach to how we handle and process data. As we witness an increasing number of connected devices and real time applications, it becomes clear how significant Edge Computing truly is. This paradigm not only addresses challenges related to latency and bandwidth limitations but also propels us into a new era of decentralized computing.
- The inclusion of Edge Computing in our technological world brings forth a future where data is not limited to far away servers but gets processed at the edge, promoting adaptability and promptness. As different sectors embrace this change, be it healthcare or manufacturing and more, Edge Computing is ready to redefine the potential of what we can accomplish in terms of digital transformation.
- FAQ
- 1.What does edge computing mean in simple terms?
- Edge Computing | Accenture
- Edge computing is a new way of computing that involves various networks and devices located near or at the user’s location. The concept of edge computing revolves around processing data closer to its source, which enables faster and more efficient processing, resulting in real time action oriented outcomes.
- 2.Can you provide an example of edge computing?
- 7 Edge Computing Examples You Should Know | The New Stack
- Another illustration of an edge computing device can be found in the field of security, particularly when it comes to ensuring worker safety. This involves using data from on site cameras, safety devices and sensors to prevent unauthorized access to the premises and monitor employees adherence to safety protocols.
- 3.What are the answers related to edge computing?
- Edge computing refers to the practice of processing, analyzing and storing data closer to where it is generated. This approach facilitates rapid analysis and response in almost real time. In recent years, some companies have centralized their data storage and computation in cloud systems as a means of streamlining operations.
- 4.How is edge computing utilized?
- Edge computing enables devices located remotely or at the periphery of a network to process data locally. This can be achieved either by utilizing the device’s own capabilities or through a nearby server.
- When data needs to be processed in the central datacenter, only the crucial information is sent to minimize any delays.
- 5.Can you please explain what EDGE stands for?
- EDGE stands for Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution. It is a digital mobile phone technology that enables faster data transfer rates. It serves as an enhancement to the GSM cellular network.
Introduction;
In the ever changing world of information technology, the concept of Edge Computing has emerged as a game changer, reshaping how we analyze and process data. Traditionally, computing power was centralized in data centers. However, with the growing need for real time and low latency processing, Edge Computing has become a pivotal paradigm.
What is Edge Computing?
Unlike conventional cloud computing that relies on distant data centers, Edge Computing brings computational capabilities closer to where data is generated. This enables faster decision making and improved performance.

In this exploration of Edge Computing, we will delve into the core principles that drive this shift in paradigm. We will discuss the decentralized distribution of computing resources and the integration of edge devices with the Internet of Things (IoT).
1. Overview;
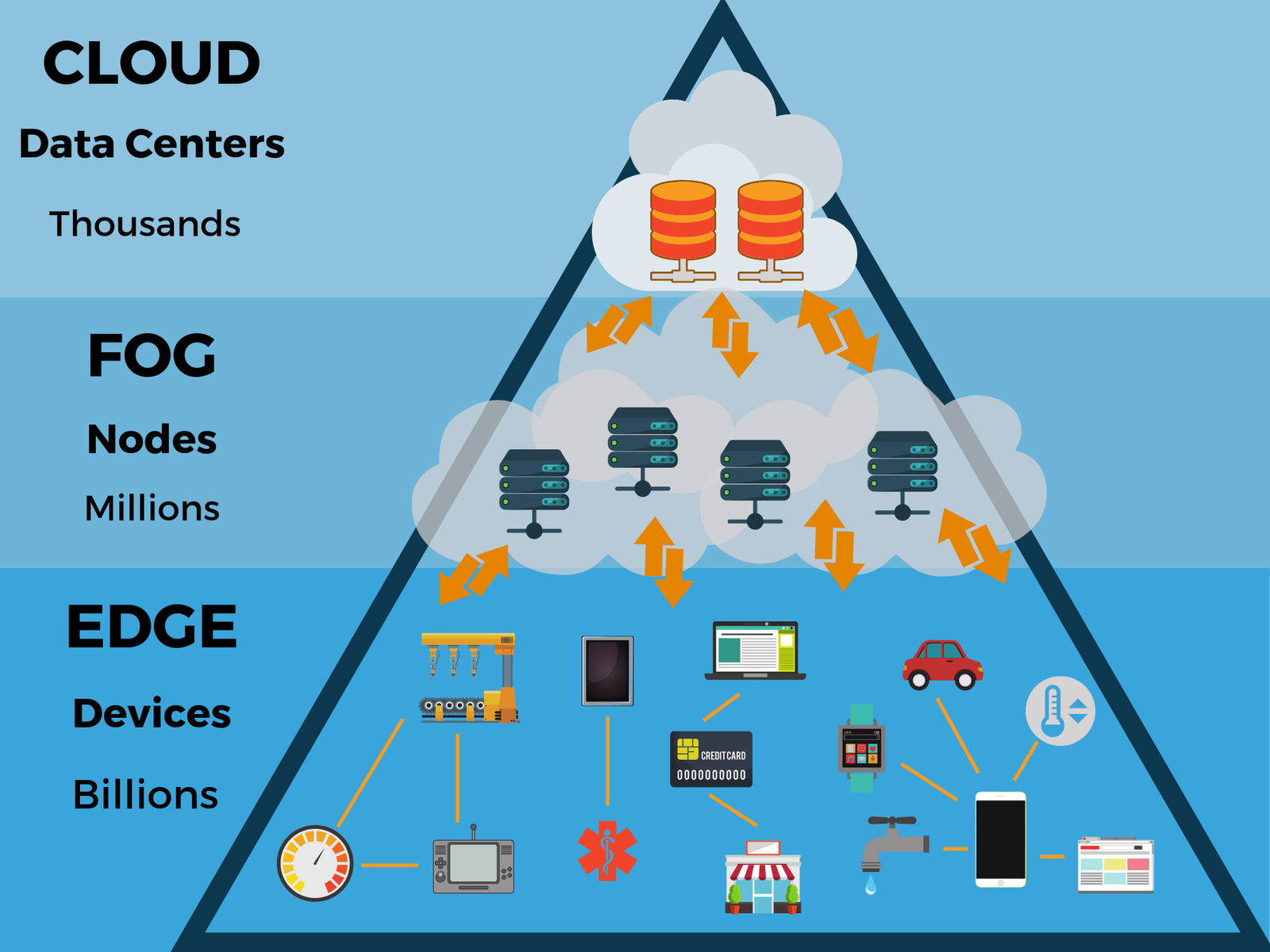
Definition; Edge Computing is a distributed computing paradigm that brings computational processes closer to the data source or “edge” of the network, rather than relying on a centralized cloud based system. The objective is to minimize delays, enhance real time processing and optimize the efficiency of data intensive applications.
2.Key Components;
Edge Devices; These are physical devices situated near the data source, such as sensors, IoT devices and smartphones. They possess computational power to process data locally.
Edge Servers/Gateway Devices; Positioned at the network’s periphery, these devices collect and preprocess data before transmitting it to the central data center or cloud. They act as intermediaries between edge devices and the cloud.
Cloud; While Edge Computing emphasizes local processing, it often collaborates with the cloud for tasks that benefit from centralized computing power, storage capacity or long term analytics.
3.Advantages of Edge Computing;
Reduced Latency; By processing data in proximity to its source, Edge Computing significantly minimizes latency. This enables real time or near real time responses crucial for applications like IoT, autonomous vehicles and augmented reality.
Bandwidth Optimization;
Edge Computing helps minimize the need to transfer large amounts of raw data to central servers, which in turn optimizes network bandwidth and reduces congestion.
Improved Security and Privacy; By processing data locally, Edge Computing enhances security by minimizing the exposure of sensitive information during transmission. It also provides better control over data privacy compliance.