Table of Contents
- Introduction:
- Intranet is a powerful tool that has transformed the way organizations operate internally. It’s like a private corner of the internet, restricted to a specific group, typically within a company or institution. This internal network enables employees to share information, collaborate on projects, and access essential resources securely. In this era of digital connectivity, intranets have become indispensable for enhancing productivity and communication within organizations.
- Intranet is like a private version of the internet used by a specific organization or company. It’s a network of computers and web pages that are only accessible to the people within that organization. Intranets are used for sharing information, documents, and resources among employees and can include things like internal websites, email systems, and file sharing. It helps employees collaborate and access company-related information securely.
- Features of Intranet
- Internal Communication; Intranets provide a convenient and efficient way for employees to exchange messages, emails and chat with each other, promoting faster and smoother communication within the organization.
- Document Sharing; With intranets, you have the ability to upload and share important documents, files and resources with your colleagues. This makes collaboration on projects easier and ensures easy access to vital information.
- Company News; Intranets often feature a dedicated section for company news and updates. This keeps employees well informed about the latest happenings within the organization.
- Calendars and Scheduling; Many intranets offer shared calendars that facilitate efficient scheduling of meetings, events and deadlines for teams.
- Search Functionality; Intranets come equipped with search bars that function like a mini Google specifically tailored for your organization. This enables you to quickly locate the documents or information you require.
- Security; Intranets prioritize privacy and security by ensuring that only authorized personnel can access sensitive information. This safeguards valuable data from unauthorized access.
- Employee Directory; You can easily find a directory of employees along with their contact details on most intranets. This makes it effortless to reach out to colleagues when needed.
- Customization; Intranets can be tailored to suit the unique needs of an organization. The option to add specific features or tools allows companies to create an intranet that aligns perfectly with their requirements.
- Mobile Access; Many intranets provide mobile app accessibility, enabling employees to stay connected even while away from their desks.
- How do intranets work?
- Feedback and Surveys; Certain intranets offer features that allow employees to provide feedback or participate in surveys to gather their opinions and suggestions.
- Intranets function by establishing a dedicated digital network within an organization. Here is a simplified description of their operations;
- Setup; An organization establishes an internal server or utilizes a cloud based system to host its intranet. This server serves as the repository for all the necessary digital information and tools essential for the smooth functioning of the intranet.
- Access Control: Access to the intranet is restricted to authorized users within the organization. Employees typically need usernames and passwords to log in.
- Data Storage: Important documents, resources, and tools are stored on the intranet server, making them accessible to employees.
- Communication: Intranets include communication tools like email and messaging systems, allowing employees to send messages and collaborate with colleagues.
- Web Pages: Intranets often have internal web pages with news, announcements, and links to various resources.
- Security: Intranets are designed with security features to protect sensitive information and prevent unauthorized access.
- Updates: Organizations can regularly update and expand their intranets to meet changing needs.
- Advantages of using an intranet
- There are several potential benefits to incorporating an intranet in a business setting;
- Enhanced communication, information sharing and collaboration within the organization.
- Simplified management of records and documents.
- Streamlined tracking of requests and tasks.
- A platform for testing out new ideas before implementing them on the company’s public website.
- Improved corporate culture that prioritizes employee engagement, participation and interaction.
- Cost effective implementation and operation leading to a favorable return on investment.
- Disadvantages associated with an intranet
- Implementing an intranet also presents some challenges to consider;
- Low user participation rates can hinder the availability of valuable content, communication and documents that make the intranet truly beneficial.
- The high cost of personnel may result in inadequate support for users when addressing software bugs or other issues promptly.
- Regular inspection and maintenance checks are necessary to ensure optimal network functionality and up to date content.
- Complexities arise when there is no clear ownership structure or when responsibilities are distributed across various groups within the organization.
- Limited support for mobile devices and remote access can pose problems for remote workers trying to access information on the intranet.
- Difference between extranet and intranet
- Extranet and intranet are both private computer networks used by organizations, but they serve different purposes and have distinct characteristics. Here are the key differences between them:
- Accessibility:
- Intranet: An intranet is a private network accessible only to an organization’s internal employees, staff, or members. It is typically restricted to users within the organization’s physical location or authorized remote access.
- Extranet: An extranet extends beyond an organization’s internal network to include authorized external users such as clients, partners, suppliers, or customers. It allows limited access to specific resources for external parties.
- Users:
- Intranet: Intranets are for internal use, enabling employees to communicate, collaborate, and access internal information and resources.
- Extranet: Extranets involve collaboration with external entities. They allow sharing of information and resources between an organization and its external partners or stakeholders.
- Purpose:
- Intranet: Intranets focus on enhancing internal communication, collaboration, and information-sharing among employees. They often host company news, documents, and internal tools.
- Extranet: Extranets are designed for secure, controlled collaboration and information exchange between an organization and external entities. They support activities like sharing project data with clients or allowing suppliers to access inventory information.
- Security:
- Intranet: Intranets prioritize internal security, and access is typically limited to employees with authentication measures like usernames and passwords.
- Extranet: Extranets require robust security measures to protect sensitive information shared with external parties. Access is carefully controlled and may involve encryption and secure authentication methods.
- Content:
- Intranet: Intranet content is usually internal, including employee directories, internal memos, company policies, and collaborative tools.
- Extranet: Extranet content may involve a mix of internal and external information, such as shared project files, customer-specific data, or partner resources.
- Conclusion:
- Additional FAQ
- 1.What do you mean by intranet?
- What is an Intranet? Definition, Benefits and Features
- An intranet is a private network contained within an enterprise that is used to securely share company information and computing resources among employees. An intranet can also be used for working in groups and teleconferences. Intranets encourage communication within an organization.
- 2.What is intranet and LAN?
- Intranet and LAN is almost one and the same thing. Almost every LAN network is an Intranet. LAN is a local network whereas Intranet doesn’t have to be local, it can be a network within a company with 3 different offices which are all inter-linked with a WAN (Wide Area Network).
Introduction:
Intranet is a powerful tool that has transformed the way organizations operate internally. It’s like a private corner of the internet, restricted to a specific group, typically within a company or institution. This internal network enables employees to share information, collaborate on projects, and access essential resources securely. In this era of digital connectivity, intranets have become indispensable for enhancing productivity and communication within organizations.
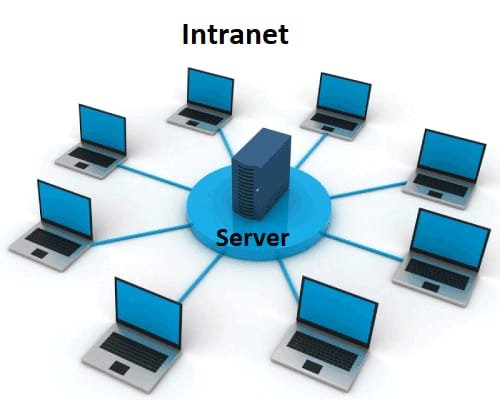
Intranet is like a private version of the internet used by a specific organization or company. It’s a network of computers and web pages that are only accessible to the people within that organization. Intranets are used for sharing information, documents, and resources among employees and can include things like internal websites, email systems, and file sharing. It helps employees collaborate and access company-related information securely.
Features of Intranet
Internal Communication; Intranets provide a convenient and efficient way for employees to exchange messages, emails and chat with each other, promoting faster and smoother communication within the organization.
Document Sharing; With intranets, you have the ability to upload and share important documents, files and resources with your colleagues. This makes collaboration on projects easier and ensures easy access to vital information.
Company News; Intranets often feature a dedicated section for company news and updates. This keeps employees well informed about the latest happenings within the organization.
Calendars and Scheduling; Many intranets offer shared calendars that facilitate efficient scheduling of meetings, events and deadlines for teams.
Search Functionality; Intranets come equipped with search bars that function like a mini Google specifically tailored for your organization. This enables you to quickly locate the documents or information you require.
Security; Intranets prioritize privacy and security by ensuring that only authorized personnel can access sensitive information. This safeguards valuable data from unauthorized access.
Employee Directory; You can easily find a directory of employees along with their contact details on most intranets. This makes it effortless to reach out to colleagues when needed.
Customization; Intranets can be tailored to suit the unique needs of an organization. The option to add specific features or tools allows companies to create an intranet that aligns perfectly with their requirements.
Mobile Access; Many intranets provide mobile app accessibility, enabling employees to stay connected even while away from their desks.
How do intranets work?
Feedback and Surveys; Certain intranets offer features that allow employees to provide feedback or participate in surveys to gather their opinions and suggestions.
Intranets function by establishing a dedicated digital network within an organization. Here is a simplified description of their operations;

Setup; An organization establishes an internal server or utilizes a cloud based system to host its intranet. This server serves as the repository for all the necessary digital information and tools essential for the smooth functioning of the intranet.
Access Control: Access to the intranet is restricted to authorized users within the organization. Employees typically need usernames and passwords to log in.
Data Storage: Important documents, resources, and tools are stored on the intranet server, making them accessible to employees.
Communication: Intranets include communication tools like email and messaging systems, allowing employees to send messages and collaborate with colleagues.
Web Pages: Intranets often have internal web pages with news, announcements, and links to various resources.
Security: Intranets are designed with security features to protect sensitive information and prevent unauthorized access.
Updates: Organizations can regularly update and expand their intranets to meet changing needs.
Advantages of using an intranet
There are several potential benefits to incorporating an intranet in a business setting;
Enhanced communication, information sharing and collaboration within the organization.
Simplified management of records and documents.
Streamlined tracking of requests and tasks.
A platform for testing out new ideas before implementing them on the company’s public website.
Improved corporate culture that prioritizes employee engagement, participation and interaction.
Cost effective implementation and operation leading to a favorable return on investment.
Disadvantages associated with an intranet
Implementing an intranet also presents some challenges to consider;
Low user participation rates can hinder the availability of valuable content, communication and documents that make the intranet truly beneficial.
The high cost of personnel may result in inadequate support for users when addressing software bugs or other issues promptly.
Regular inspection and maintenance checks are necessary to ensure optimal network functionality and up to date content.
Complexities arise when there is no clear ownership structure or when responsibilities are distributed across various groups within the organization.
Limited support for mobile devices and remote access can pose problems for remote workers trying to access information on the intranet.
Difference between extranet and intranet
Extranet and intranet are both private computer networks used by organizations, but they serve different purposes and have distinct characteristics. Here are the key differences between them:
Accessibility:
Intranet: An intranet is a private network accessible only to an organization’s internal employees, staff, or members. It is typically restricted to users within the organization’s physical location or authorized remote access.
Extranet: An extranet extends beyond an organization’s internal network to include authorized external users such as clients, partners, suppliers, or customers. It allows limited access to specific resources for external parties.
Users:
Intranet: Intranets are for internal use, enabling employees to communicate, collaborate, and access internal information and resources.
Extranet: Extranets involve collaboration with external entities. They allow sharing of information and resources between an organization and its external partners or stakeholders.
Purpose:
Intranet: Intranets focus on enhancing internal communication, collaboration, and information-sharing among employees. They often host company news, documents, and internal tools.
Extranet: Extranets are designed for secure, controlled collaboration and information exchange between an organization and external entities. They support activities like sharing project data with clients or allowing suppliers to access inventory information.
Security:
Intranet: Intranets prioritize internal security, and access is typically limited to employees with authentication measures like usernames and passwords.
Extranet: Extranets require robust security measures to protect sensitive information shared with external parties. Access is carefully controlled and may involve encryption and secure authentication methods.
Content:
Intranet: Intranet content is usually internal, including employee directories, internal memos, company policies, and collaborative tools.
Extranet: Extranet content may involve a mix of internal and external information, such as shared project files, customer-specific data, or partner resources.